Risk
Risk Definition
- [i] Risk) - (definition:: The likelihood or probability of a loss, damage, or compromise to an organization's assets) - (subject:: Cybersecurity
Risk Information
The higher the risk, the higher the potential for adverse consequences. Risk can be deliberate and malicious, like a cyber attack, or unintentional, like an employee accidentally leaving a door propped open. Regardless of intent, any violation of an organization's security is a breach. Risk is closely related to Impact.
This is called a Risk Matrix:
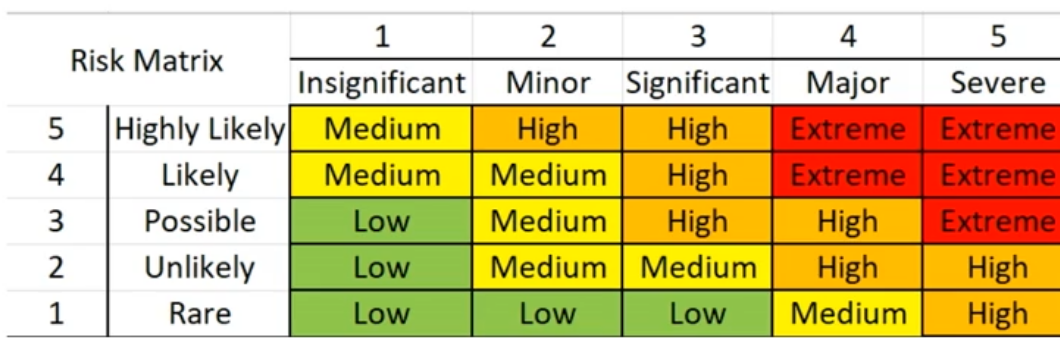
The x axis of this table is severity, and the y axis is the likelihood. This is a simple version of a risk matrix which is used by organizations. A risk assessment is another example of this.
Risk Management (or Mitigation)
A commonly used framework for risk management is the NIST Risk Management Framework (RMF):
- Prepare: Establish the context and activities needed to manage security and privacy risks
- Categorize: Categorize the system and information that is processes, stores, or transmits.
- Select: Select the security and privacy controls to protect the system.
- Implement: Implement the selected controls and document how the controls will be deployed
- Assess: Assess the effectiveness of the implemented controls
- Authorize: Authorize the system to operate based on the risk assessment.
- Monitor: Continuously monitor the system and the controls.
This approach helps organizations identify, prioritize, and address risks they face, instead of eliminating all risk, which is often not feasible.